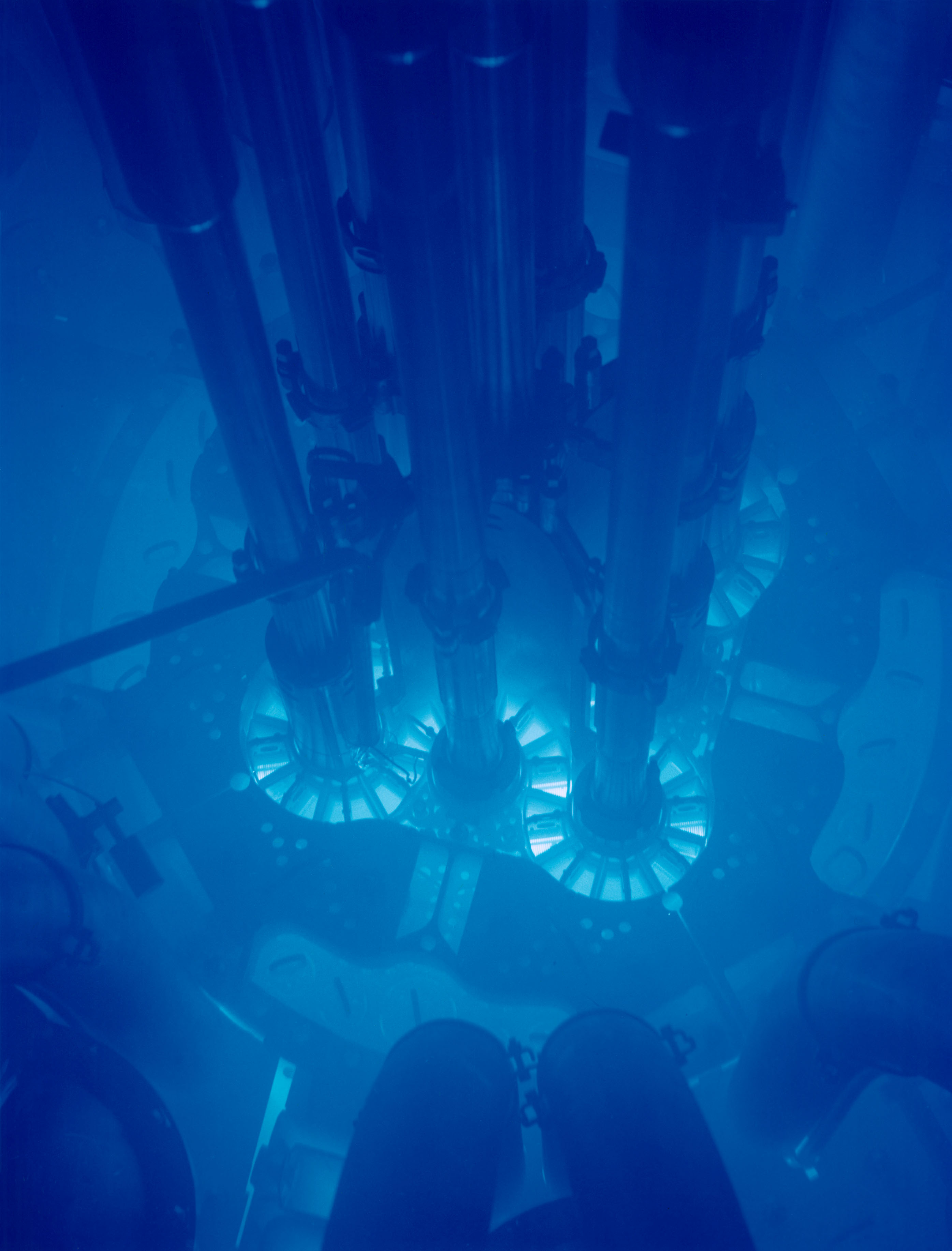
The Cerenkov effect is the light equivalent of a sonic boom (the noise heard when an object travels faster than the local speed of sound, e.g. the crack of a whip). When an object travels faster than the local speed of light (e.g. a high energy positron), a flash of blue light is emitted. This is the reason for nuclear reactors' eerie blue glow, and Watchmen character Doctor Manhattan's distinctive blue skin.
Cerenkov light is seen in nuclear reactors due to the nature of radioactive material they use. If the material decays by emitting a particle such as an electron or positron (Beta decay) as opposed to a photon (Gamma decay), chances are a large proportion of these particles will be traveling fast enough to satisfy the Cerenkov condition, i.e. faster than the speed of light within the radioactive material. This is why fuel rods and surrounding water (since the decay particles may be also traveling faster than the speed of light in water) appear to glow blue.





No comments:
Post a Comment